What is GSR
GSR is the abbreviation of Green and Sustainable Remediation. According to the definition announced by Taiwan EMA, Green and sustainable remediation(GSR) is “Any technique, strategy, or management plan that considers environmental, economic and social aspects, which can reduce environmental footprints, negative social economic impacts throughout the remediation process, from site investigation, remedy design, operation and management to site closure, while still meeting the regulatory requirements.”
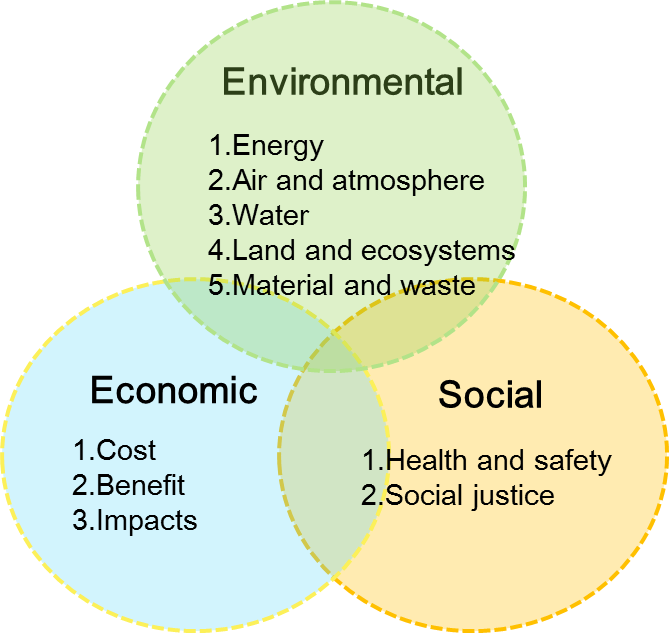
Figure Instruction:
Core elements for the environmental aspect include energy, air and atmosphere, water, land and ecosystems, and material and waste. For the economic aspect, core elements include cost, benefit and impacts. For the social aspects, core elements include health and safety and social justice.
Why should we adopt GSR?
Although the purpose of site remediation is to cleanup contamination in order to protect the environment and human health, site activities during the course of remediation may cause secondary impacts. For example, equipment operation will produce air pollution and GHGs emission. In addition, VOCs emission due to excavation during the construction of the remedial system may create potential health risk and noise disturbance to the local neighborhood. For the economic aspect, GSR encourage economy promotion and job creation.
Currently in Taiwan, polluters intend to select a quick remediation method to delist the site. However, those methods often consume more energy and resources, meanwhile generating secondary pollutions. Complying GSR in remediation works is helpful for reducing the impacts on abovementioned aspects to realize sustainable utilization of soil and groundwater.
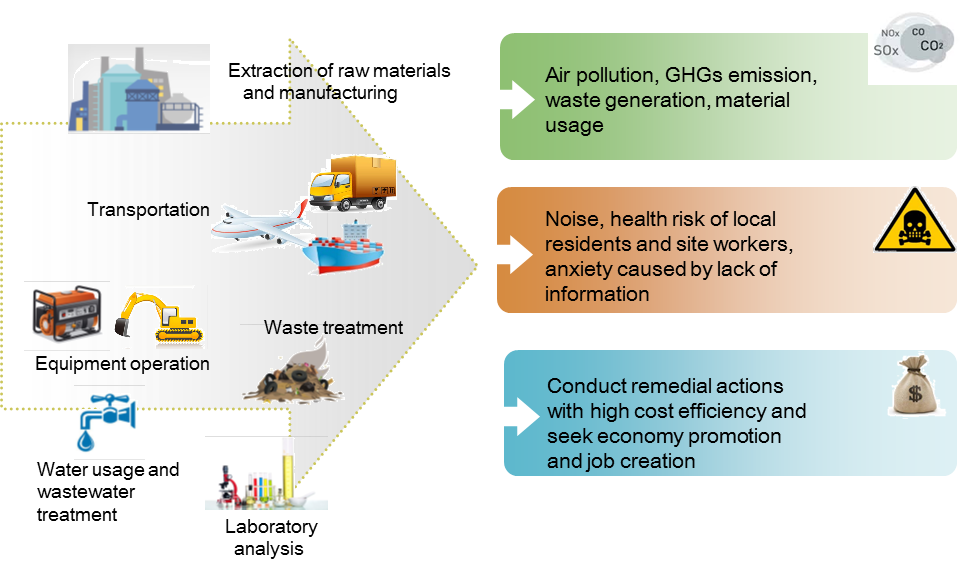
Figure Instruction:
Although the goal of site investigation and remediation is to solve contamination problems. Site activities throughout the life-cycle of cleaning up a site may create adverse secondary impacts. Such as extraction of raw materials and manufacturing, transportation, equipment operation, Waste treatment, water usage and wastewater treatment etc.
When should we adopt GSR?
Generally, GSR can be incorporated into any phase of the site cleanup process. Based on the evaluation goal, GSR assessment can be classified into two categories. If the site hasn’t chosen a remedy, the goal of a GSR assessment is to compare different alternatives and select a comparatively sustainable remedy. For sites with a selected remedy or sites already executing the remedial plan, the goal of GSR is to evaluate the current situation of the site and find “hot spots ”of impacts to mitigate negative effects.
How to conduct GSR?
In the beginning of remediation, when remediation methods are not determined yet. Environmental, economic and social assessment tools can be used to evaluate the performance of different remedies. The GSR decision supporting system can be applied to compare different remediation methods by comprehensively considering the assessment results.
If the remediation methods of a site is determined, the environmental footprint assessment tool be applied to reveal the “hot spots” of remediation activities. A streamlined Best Management Practices (BMPs) selection tool is also available for users to find optimization strategies of site management in order to reduce negative impacts.
Recommended GSR assessment measures are summarized as below.
- Environmental: Analyze energy, resource consumption and other environmental footprints through life-cycle assessment principles.
- Social: Considering health and safety of stakeholders by conducting human health risk assessment. Ensure public involvement and the right to know of local residents.
- Economic: Conduct remedial actions with high cost efficiency and seek economy promotion and job creation.
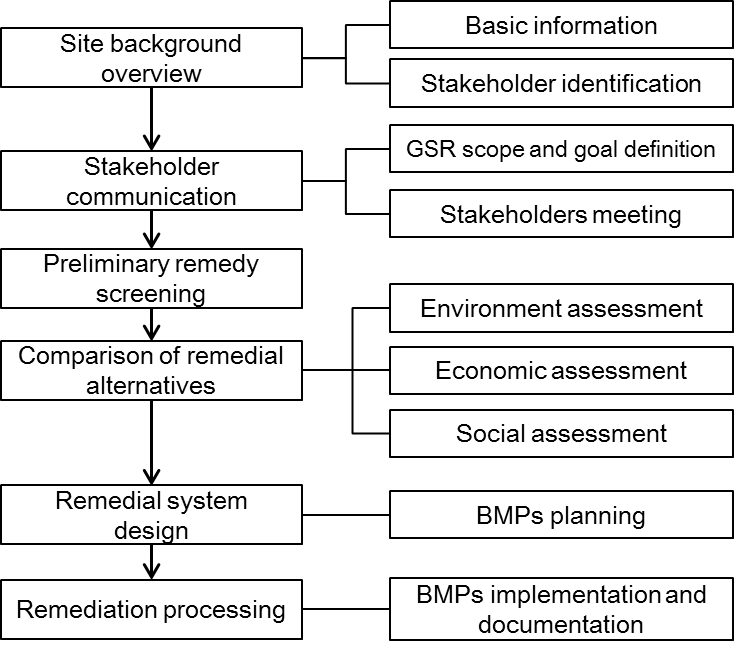
Figure Instruction:
If the site hasn't chosen a remedy, the goal of a GSR assessment is to compare different alternatives and select a comparatively sustainable remedy.
A GSR assessment for this type of site will start with site background overview, which historical investigation results and related reports will be reviewed. Stakeholder communication would take place to determine the scope and goal of the assessment.
In the preliminary stage, responsible parties should screen possible alternatives based on technical, financial and time feasibility. The remaining alternatives can then be compared according to the environmental, economic and social performance. Stakeholders will be able to select the most suitable remedy for site remediation.
GSR continues in the implementation of the selected remedy. Site managers should plan Best management practices to meet the GSR core elements.
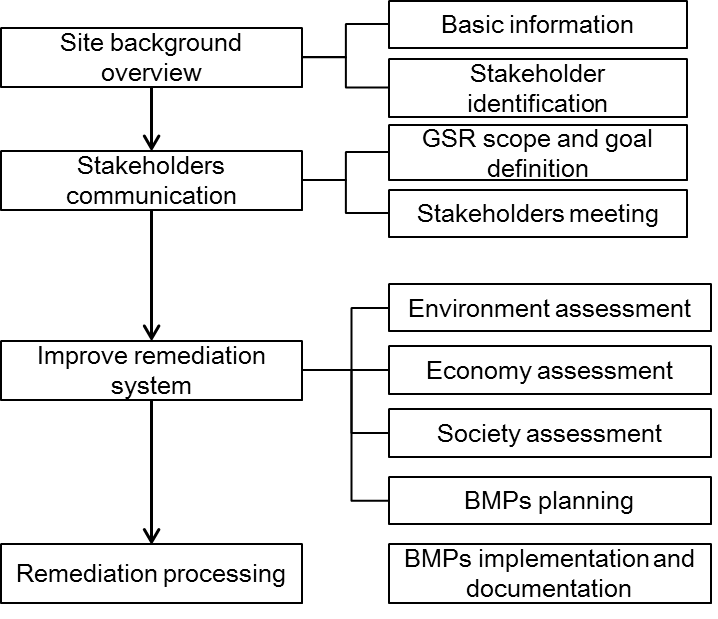
Figure Instruction:
For sites with a selected remedy or sites already executing the remedial plan, the goal of GSR is to evaluate the current situation of the site and find "hot spots "of impacts to mitigate negative effects. Best Management Practices (BMPs) can then be implemented to optimize the remediation system.
Remedy selection decision supporting tool
If the remediation method of a site is not determined, site managers can select the remedy by evaluating the environmental, social and economic performances of different alternatives and involve stakeholders to participate in the decision making process.
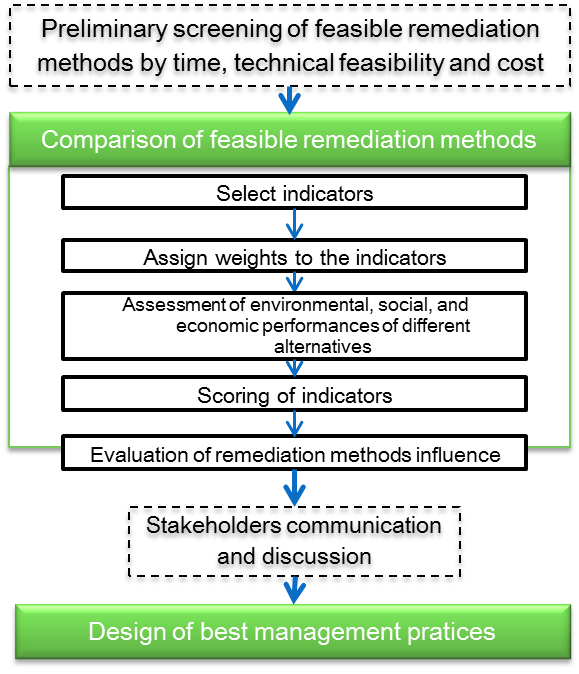
Figure Instruction:
he 5 steps of the GSR remedy selection supporting system are
1.Selecting indicators
2.assigning weights to indicators
3. Assessment of environmental, social and economic performances of different alternatives.
4. Scoring of indicators
5. Final remedy comparison based on the overall score
The core elements and principles of GSR
Core elements of Environmental, economic and social aspects are established under the GSR framework. For the environmental aspect, core elements include reduce energy consumption, reduce air pollution, minimize water usage, impacts on soil and ecosystems, reduce material and wastes. Core elements of the economic aspect include cost, benefit, and impacts. Social core elements are composed of health and safety and social justice. Each core element can be divided into several principles, for instance, the core element "reduce energy consumption" includes adopt energy-saving measures, usage of renewable energy and enhance energy efficiency. The core elements and principles of GSR are as the table below, all of the content and evaluation of GSR should be in accordance with these core elements and principles.

Core elements of Environmental, economic and social aspects are established under the GSR framework. For the environmental aspect, core elements include reduce energy consumption, reduce air pollution, minimize water usage, impacts on soil and ecosystems, reduce material and wastes. Core elements of the economic aspect include cost, benefit, and impacts. Social core elements are composed of health and safety and social justice.
Quantitative tools
- Environmental:Environmental footprint assessment tool
- Social:Resident questionnaire, health risk assessment
- Economic:Cost, benefit and economic impacts analysis
Qualitative tools
Best Management Practices screening tool
GSR history
The GSR concept was introduced by the Taiwan EPA in 2008. The Taiwan EPA paid high attention on collecting the related information on globally sustainable remediation developing current state and tools since 2012. Consequently, the framework of GSR in Taiwan, assessment tools and promotion strategies were gradually promoted.
Environmental, economic and social assessment tools and a BMPs screening list were established in 2013. In order to enhance the promotion of GSR, The EPA also held many workshops to demonstrate the GSR concept, evaluation process, and applicable tools. So far, more than 5 contaminated sites in Taiwan had participated in GSR assessment and proposed feasible BMPs to improve their remediation work.
Taiwan EMA is dedicated on promoting GSR and the improvement of assessment tools. Contaminated sites are encouraged to make comprehensive considerations when executing remediation work by using GSR related assessment tools so that soil and groundwater protection can be both effective and sustainable.